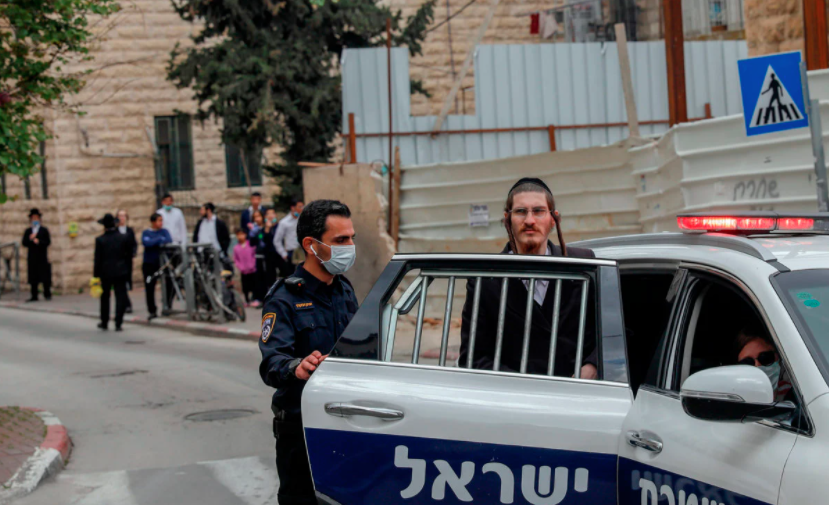
(The Conversation) — Police broke up a funeral for an Orthodox Jewish rabbi in Brooklyn on April 28, with New York City mayor Bill de Blasio calling the event – which violated coronavirus restrictions on large gatherings – “absolutely unacceptable.”
Most prominent rabbis around the world support government regulations intended to curb the spread of coronavirus, even if it means closing places of study and worship. But some observant Jewish communities in the United States and Israel have been slow to adopt social distancing.
You may unsubscribe from any of our newsletters at any time.
The leader of a strictly observant Jewish community elsewhere in New York instructed his followers to continue collective study and prayer well into March, though COVID-19 had already killed thousands in the state.
In Israel, an observant Jewish neighborhood has reacted with defiance – even violence – to the country’s strict social distancing regulations.
Outsiders are often outraged when religious communities defy policies meant to protect the general public.
As an anthropologist who studies religion, politics, identity and conflict in Israel and Palestine, my research helps explain why some strictly observant Jewish communities disobey public health guidelines – and why it’s more complicated than simply flouting the rules.
Who are Haredi Jews?
Ultra-Orthodox, or Haredi Jewish communities, are a diverse population, with varying spiritual and cultural practices. But they all follow Halacha, loosely translated as Jewish law.
As such, many do not share the same information sources that others take for granted. In accordance with the rulings of their rabbis, internet access, television broadcasts and certain cellphone functions are generally limited in strictly observant Jewish communities.
More on Broadview: Passover seders get creative twists
Maintaining their closeness to God by distancing themselves from the secular world prevented many Haredim from seeing news reports of the virus spreading worldwide in February and March.
Some Haredi leaders maintained that gathering to pray and study remained paramount. Studying the Hebrew scriptures, or Torah, is a commandment and a duty in Judaism. Haredi men generally gather to pray three times daily. Students at yeshivas, or Jewish seminaries, may spend 18 hours a day studying together.
More than a way of life, prayer and study are the means for protecting life itself. According to Jewish sages, “One who engages in Torah study also protects the entire world.” Indeed, “without Torah the world falls.”
The importance of engaging with the Torah explains why one prominent rabbi in Israel insisted even in March that “cancelling Torah study is more dangerous than the coronavirus.”
Ultimately, the Israeli government intervened to enforce its coronavirus restrictions. On March 22, police were sent into Me’a She’arim, a Haredi neighborhood in Jerusalem, to end public gatherings, close synagogues and shutter schools.
They were met with curses, slurs and thrown stones. Some Haredim even called the Israeli police “Nazis.”
Collective memory
While such responses might seem extreme to outsiders, they become clearer when considering Jewish history and the memories provoked by police intervention.
Anthropological research demonstrates that people give meaning to their experiences in different ways. Our perception, imagination and actions are deeply embedded in the whole of our experiences. The past – whether individually experienced or collectively nourished by the community – gives meaning to the present.
Henri Bergson, a French philosopher, used the term “duration” to explain how the past shifts to present itself in ways that appeal to current experiences in different ways for different people.
The importance of engaging with the Torah explains why one prominent rabbi in Israel insisted even in March that “cancelling Torah study is more dangerous than the coronavirus.”
In times of crisis like the coronavirus pandemic, this sense of duration becomes more acute.
For some, hospital tents erected in public places evoke World War I. A Holocaust survivor recently told me the stay-at-home order brought back memories of her childhood years of confinement hiding from the Nazis. One New Orleans resident found that the “flood” of coronavirus deaths recalled Hurricane Katrina.
Duration as personal memory is central to an individual’s sense of self, but it arises in collective memories, too.
Collective memory, including the stories we all tell ourselves and our children about our past, gives meaning and purpose to our collective selves. These stories recount struggles and triumphs and help define our moral community.
Duration interacts with collective memory, and is key to the formation of group identity.
History of persecution
The historical persecution of Jews around the world is central to both secular and strictly observant Jews. However, how that memory works in contemporary circumstances is not predetermined. My research demonstrates that different aspects of the past inform collective meaning and actions differently.

Unlike most Israelis – who see Jewish history as a justification for the state of Israel and understand the Israeli army and police as existing to protect them – some Israeli Haredim distrust the government and its functionaries.
In fact, Haredi Jews, who make up about 10 percent of Israel’s population, are foundationally opposed to Zionism, the political ideology of Jewish nationalism that led to the establishment of Israel in 1948.
While Haredi Jews believe that God promised the land of Israel to the Jewish people, they are also certain that promise cannot be fulfilled by human intervention in God’s work, such as the establishment of a nation state. They have previously clashed with the Israeli government and law enforcement over compulsory military service and other policies.
Suspicion of police
So when armed men in uniform entered their neighbourhoods to close down synagogues and yeshivas, members of the Haredi community drew on their collective memories of soldiers and police wreaking havoc and destruction on Jewish communities in Tsarist Russia and later in Western Europe. Rather than feeling protected by the state, they were fearful and suspicious.
Suspicion of the police is common in other communities historically mistreated by law enforcement. The collective memories of both black Americans and the Roma of Europe, for example, associate police with violence and danger.
When facing a crisis like the coronavirus, many people rely primarily on science, technology and governments for protection. And the Haredim do not reject science or medicine.
But for them, living the Torah life through daily study and prayer is the primary means by which all human life is maintained and preserved. When the political order interferes with their work, the consequences could be more disastrous than a pandemic. It could mean the end of Jewish life, if not of humanity itself.
You need to understand the coronavirus pandemic, and we can help. Read The Conversation’s newsletter.
Joyce Dalsheim is an associate professor of global studies at the University of North Carolina Charlotte. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.